Prototyping in UX [Sketching]
The best prototype is the one that, in the simplest and most efficient way makes the possibilities of a design idea visible and measurable.
THE UX BASICS
Have you ever wondered how we get hooked to certain websites and spend hours without realising it? Or, how it becomes so easy to navigate between some websites while with others it’s simply annoying even to identify the provided action items. So what makes these websites or products stand out? The answer to all these questions is a better User Experience Design. So grab a cup of coffee and let’s know, how, when and where we can use UX to make our products stand out by focusing on the User as the primary source of inspiration.
The best prototype is the one that, in the simplest and most efficient way makes the possibilities of a design idea visible and measurable.
And this can be applied in the design process, by choosing the prototype that is most appropriate for the phase of design to answer the questions that are critical at that time.
Basically, US is how the end product gonna look like
Basic Types of Prototype:
There are a few different kinds of prototype making.
Verbal description
Sketch
Video
Navigation Flow
Storyboards: User story
Physical Model
Card-based: Sequence of interaction or Actions
But we can actually categorize these prototypes in different types:

Here is the feature list:

Lo-Fid prototype is quick, cheap and easy to use. It maximizes the possibility of refinement. Exp: Pen paper sketch
Mid-Fid prototype is more organised and gives a narrative of the whole system in a cheap and affordable way. Exp: Wireframes
Hi-Fid prototypes are more implementation focused and gives emphasis on interaction and functionality. Exp: Mocked Elements / Beta Prototype
4 steps to design the prototype:

Reification: Make the prototype real.
Reflection: Reflect if the prototype is gonna work.
Communication: Review the prototype
Assessment: Like assessing beta testers to understand if it’s gonna satisfy user needs
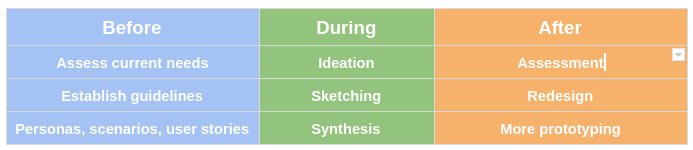
Features of Prototype:
A prototype can be either horizontal design or vertical design.
**Horizontal (**Design all in brief)
- All of the features are designed in brief and the designs might not be very accurate.
Vertical (Design few in-depth)
- A few features are designed in-depth and the designs need to be very specific
So the priority queue for designing any prototype will be:

We should always start with Lo-Fi prototype design. Otherwise, it will be a waste of money and effort. It will simply exhaust resources, cognitive and emotional commitments.
Pen Paper (Lo-Fid)
“Sketching in the broad sense is an activity not just a byproduct of design. It is central to design thinking and learning. Sketches are a byproduct of sketching. They are part of what both enables and results from the sketching process but there’s more to the activity of sketching than making sketches.” — Bill Buxton
Why do the pen-paper sketch??
Why should we sketch and do not go into prototype development? Simple isn’t it?
Cheap
Quick
Timely
Inexpensive
Disposable: can dispose when of no use
Plentiful: can make as much as we want
Minimal detail
Allows ambiguity
How does it help us?
Help reflect the idea better
Helps explore more designs
Helps communicate with others about the idea
How to design??
Very simple, pen and paper (Do not use Softwares. It will just intimidate you with all the detailing). And most importantly, you don’t have to be good at drawing.
Sketches Generate Possibilities and Prototype converge the possibility to fix a design

Build, don’t stop. If intimidating? Brainstorm in the team.
The layout matrix thinking might help with speeding up ideation
Ideation techniques: If you can’t think a good idea, think bad ones (Take inspiration from bad products)
Designing Improvement:
The designs will even be better if we keep a few more things in mind. Like:
Improving the prototype for individuals or a group
Keeping in mind the cultural and social value
Designing Alternatives:
It is very important to keep alternative designs in mind to make the prototype more advanced. Often it’s difficult to bring more new ideas into the canvas so keeping a few points into consideration while designing will help create more and more ideas. For example:
The explicit need of user (as they say)
The implicit need of the user
What system should do: Functional Requirements
Constraints on the system and its development: Non Functional Requirements
Other prototyping
Wizard of OZ: Human pretending to be computer
Proof of Concept: Producing video featuring the features and applications
Metaphor Technique: Build a mental model- linking the design with something already existing
Tools for prototyping:
So that’s it for this article. I hope you all liked it and if you liked it then do not forget to tell us your thoughts in the comment section below.
If you want to connect with me, here I am at Twitter or Instagram
Follow our community LinkedIn group, Facebook Page and Twitter for more such articles and posts and meet like-minded people to collaborate.

![Prototyping in UX [Sketching]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1688665405864/6dadd735-941e-4a59-9a07-939ce871d966.png?w=1600&h=840&fit=crop&crop=entropy&auto=compress,format&format=webp)